Many people ask: how long does ketamine stay in your system? Ketamine, also referred to as ‘Ket’, ‘Special K’, or simply ‘K’, is a powerful hallucinogenic drug. Ketamine is typically available in powder form, which may be snorted or swallowed as a tablet, but it may also be injected in liquid form. The drug was initially developed to be used in healthcare or veterinary settings to provide pain relief during human and animal surgeries, as it also has strong anesthetic effects. Ketamine can start working within minutes after being abused, and its effects can last from 30 to 60 minutes.
History of Ketamine
A dissociative anesthetic, ketamine is used to induce and maintain anesthesia in healthcare settings. It is also used as a recreational drug. Unlike opiates, ether, and propofol, it does not suppress respiration or heart rate, making it one of the safest anesthetics. Ketamine may be used to treat and cure treatment-resistant depression at lower, sub-anesthetic doses. Long-term use of ketamine is associated with unknown long-term consequences and is an area of active research.
It’s been used extensively in veterinary medicine and as a surgical anesthetic in Vietnam War, but it was first synthesized in 1962 and approved for use in the United States in 1970. The powder and liquid forms of ketamine are often referred to as ‘Special K’ because of their hallucinogenic and dissociative effects when they’re used as recreational drugs.
How Does Ketamine Make You Feel?
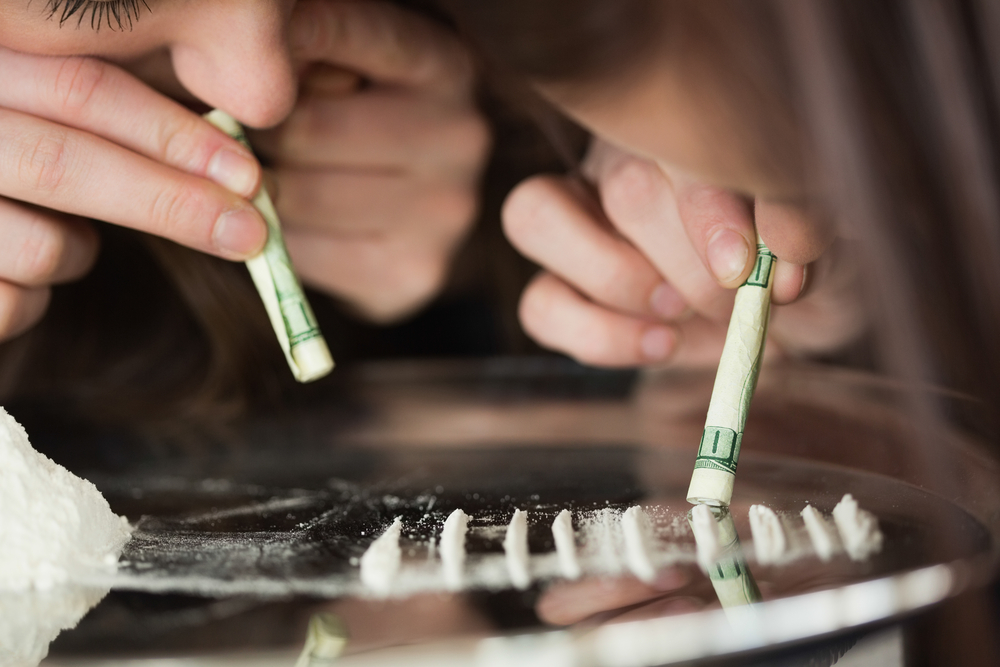
When someone takes Ketamine, they experience euphoria and calmness. Many Ketamine addicts compare their drug-taking experiences to a ‘K-hole’. People who take Ketamine hallucinate and feel detached from reality. When a person takes Ketamine, they may feel unable to move or return to reality. Many people feel as if they are floating and disconnected from reality. Ketamine may be snorted as a powder, mixed with liquid and swallowed, swallowed in a capsule pill, or injected. It is manufactured as a white powder and sold illegally. It is not unusual for drug dealers to steal Ketamine from Veterinarian clinics or hospitals.
The most typical method of taking Ketamine is by snorting or consuming it. A person seeking to get high on Ketamine might take up to 300 milligrams. The higher the dosage, the more profound the consequences and the lengthier the period of time that the person is high. Ketamine is a close relative of phencyclidine (PCP), yet it is not as strong as pure PCP. PCP and Ketamine are both hallucinogenic and dissociative anesthetics that inhibit sensory perception. When people are on Ketamine, their perceptions of color, time, and space, as well as their self-awareness and their surroundings, are distorted. As a result, they might believe they can walk on water, fly, or believe other hazardous hallucinations are real.
Signs of Ketamine Abuse
There is no way to determine which dose of Ketamine would be dangerous, as people respond to it very differently. Psychological dependence is one of the major side effects of abusing Ketamine. The user builds up a tolerance to the drug over time, requiring higher doses to achieve the same results. If someone you care about is abusing Ketamine, you may notice the following signs:
- Flushed skin
- Slurred speech
- Rapid eye movements
- Depression
- Mood swings
- Insomnia
- Irritability
- Loss of coordination
Signs of Ketamine Addiction
An addiction can develop if the drug is abused over a long period of time. As the user’s tolerance to the drug increases, they will consume more of it. Psychological addiction, defined by an obsession with and voracious cravings for the drug, may result from prolonged Ketamine abuse. The following are symptoms of a Ketamine addiction:
- Problems within relationships
- Deceit
- A compulsion to acquire and use more of the drug
- Trying but being unable to quit
- Intense cravings
- Neglecting responsibilities and obligations
How Long Does Ketamine Last?
When taken as directed, ketamine is an injectable medication that begins working immediately. If injected intravenously, it begins operating in seconds; if injected into a muscle, it begins operating in four minutes. The drug’s effects last between 15 and 30 minutes. It sedates as well as relieves pain at standard doses. It causes dissociative effects that distort your perceptions and make you sense as though you are outside your environment when abused or taken at higher doses. When abused, the drug is snorted, smoked, or swallowed. Ketamine is often mixed with cocaine and ecstasy, both of which have been connected to sexual assaults. It begins working immediately and lasts 30 to 60 minutes when abused.
How Long Does Ketamine Stay in Your System?
The amount of ketamine your body absorbs is measured in a procedure known as the half-life. Your body absorbs all it can from ketamine after approximately 2.5 to 3 hours, at which point you may start to feel a comedown. Some people maintain the euphoric state they were in by taking more of the drug to avoid the comedown symptoms. While the time period of 2.5 to 3 hours may seem short, you can still be tested for ketamine after consuming it.
An adult with a healthy system will eliminate ketamine after five half-lives, which will take about three hours and 45 minutes. Everyone will differ in how long it takes their body to eliminate ketamine, but this is an average. It takes 45 minutes for ketamine to half-life. In order to eliminate a drug from the body, five half-lives must occur, so this indicates that it will take about three hours and 45 minutes in the case of ketamine. It’s critical, nevertheless, to keep in mind that ketamine may still be present on a drug test long after it’s been consumed.
Factors that Affect How Long Ketamine Stays in Your System
The duration that ketamine stays in your body depends on a variety of personal factors, including age, body mass, genetics, liver function, and overall health. An elderly person is likely to eliminate ketamine from their system more slowly than a young, healthy person. The following are other factors:
Age and Health
Younger, healthy people tend to metabolize ketamine more rapidly than older individuals, because their metabolisms are usually faster.
Levels of Hydration
Ketamine leaves your body via your urine, and therefore urinating more often if you are well-hydrated will speed the process up.
Metabolism
Individuals with a higher metabolic rate can flush away drugs like ketamine more rapidly than those with a lower metabolic rate.
Kidney and Liver Function
Your liver and kidneys are responsible for ridding your system of ketamine. If either of these organs is damaged and thus less able to carry out its duties, your system will be unable to eliminate the ketamine quickly.
Body Mass
Someone with a lower body mass may metabolize ketamine slower than someone with a higher body mass. This is because the amount of ketamine you have taken represents a smaller proportion of your overall body mass. As a result, those with higher body masses can eliminate ketamine quicker.
Dosage
The longer it takes for your body to eliminate a higher dose of ketamine, the harder your body will have to work.
Frequency of Use
Regularly abusing ketamine can cause you to consume another dose before the last one has fully left your system, resulting in a build-up in your body and slowing down the elimination of the drug.
Mixing With Other Drugs
When you take ketamine with other medicines, your body must process all of them simultaneously, resulting in a longer process.
Will Ketamine Show Up on a Drug Test?
Because standard drug tests don’t usually include ketamine, it’s unlikely that taking ketamine would make a difference. However, in some cases, ketamine is screened for. Ketamine can remain in different parts of the body for different durations. Ketamine can be detected in the following ways:
Urine
It is possible to detect ketamine and its byproduct norketamine in urine. In some instances, the drug can be detected up to several weeks after the last dosing, depending on the amount of ketamine consumed. Like most substances, larger doses of ketamine may be present in the urine for longer than lower doses.
Blood
Ketamine can be detected in blood, but blood tests for ketamine are uncommon. The fact that ketamine takes about 2.5 hours to move from the bloodstream into the body’s tissues reflects the time at which it is most likely to be detected in the bloodstream.
Hair
Hair can hold signs of ketamine use for up to three months after the drug is taken. Ingesting ketamine leaves behind specific clues in the hair for up to seven to ten days.
Ketamine Addiction Treatment at Knoxville Recovery Center
If you’re wondering how long does ketamine stay in your system or if you’ve noticed signs of ketamine addiction and are concerned about your ketamine use, you should seek professional assistance immediately. At Knoxville Recovery Center, we offer a medically assisted drug detox program for ketamine addicts, helping them to come off ketamine in a secure environment while managing their withdrawal symptoms.
Once you’ve completed detox, you’ll be able to participate in evidence-based therapy to discover the root of your ketamine addiction, build resilience for the future, and move forward with your life. Contact us today to learn more about our treatment options and how we can help you overcome your ketamine addiction.