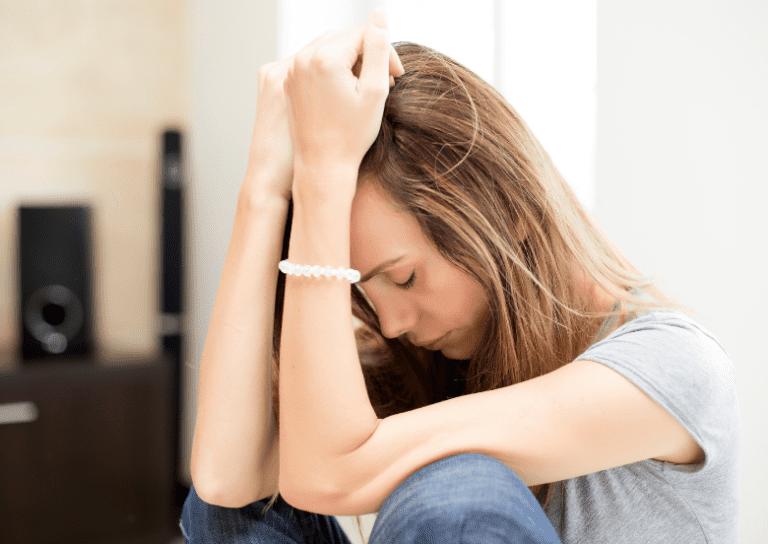
When it comes to managing anxiety and related conditions, two of the most widely prescribed medications are Ativan (lorazepam) and Xanax (alprazolam). Both belong to the benzodiazepine family—a class of drugs known for their calming effects on the nervous system. But when we look at Ativan vs Xanax, it’s important to see these drugs not only as treatment options but also as substances with a very real potential for abuse, dependence, and addiction.
In the world of addiction recovery, understanding the nuances of Ativan vs Xanax is vital. Many people begin taking these medications for legitimate medical reasons—such as anxiety, panic disorders, or insomnia—but end up struggling with dependence. Treatment centers and recovery programs regularly see clients who have developed a substance use disorder related to benzodiazepines. That’s why we need to examine the similarities, differences, risks, and long-term impacts of Ativan and Xanax through the lens of recovery.
Benzodiazepines: A Double-Edged Sword
Benzodiazepines, including both Ativan and Xanax, are classified as central nervous system depressants, meaning they slow down brain activity to create a calming effect. They work by enhancing the action of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits nerve transmission and helps regulate feelings of stress and anxiety. When GABA’s effects are amplified through these medications, individuals often experience a sense of relief from racing thoughts, muscle tension, or the overwhelming symptoms of panic.
This is why benzodiazepines are so commonly prescribed to treat anxiety disorders, panic attacks, and in some cases, seizures or sleep disturbances. For short-term use under close medical supervision, they can provide powerful relief and restore a sense of balance to someone’s mental health.
The challenge, however, is that this same calming effect can quickly turn into a double-edged sword. Because the brain begins to rely on the presence of benzodiazepines to maintain stability, tolerance develops over time. This means a person needs higher or more frequent doses to achieve the same level of relief they initially felt.
That progression creates a dangerous cycle of misuse when it comes to Ativan vs Xanax, as individuals may begin to take more than prescribed, combine the drugs with alcohol or other substances, or seek them out illegally once prescriptions run out. This dependency is not just psychological—it also alters the brain’s chemistry, making withdrawal symptoms severe and sometimes even life-threatening if the drug is stopped abruptly.
When considering Ativan vs Xanax, it’s important to recognize that both medications carry this same potential for dependence, though their differences in potency and duration of action influence how addiction may take hold. Xanax, with its rapid onset, can create a powerful reinforcement loop, making people more likely to crave repeated doses. Ativan, while slower acting and longer lasting, can still lead to the same cycle of tolerance and dependence if misused.
For this reason, understanding the risks associated with Ativan vs Xanax is critical—not only for safe use but also for shaping effective treatment and recovery strategies for those who develop a benzodiazepine use disorder.
Key Differences Between Ativan Vs Xanax
Ativan (Lorazepam)
- Primary Uses: Anxiety, insomnia, seizures, and sometimes alcohol withdrawal.
- Onset and Duration: Slower onset compared to Xanax, but its effects last longer, making it useful for extended relief.
- Addiction Potential: Because it lingers in the system longer, Ativan may produce less intense cravings than Xanax, but dependence can still form quickly with prolonged use.
Xanax (Alprazolam)
- Primary Uses: Anxiety disorders and panic attacks.
- Onset and Duration: Works quickly, providing rapid relief, but wears off faster. This often leads patients to take multiple doses per day.
- Addiction Potential: Its fast-acting nature creates a strong reinforcement cycle—people feel immediate relief and want to take it again, making Xanax particularly notorious for abuse.
When weighing Ativan vs Xanax, addiction specialists often point out that Xanax’s short half-life makes it more prone to misuse, while Ativan, though longer-acting, can also become habit-forming when used outside medical guidance.

Side Effects and Dangers of Misuse
Both Ativan and Xanax come with side effects, which can become more dangerous when the drugs are misused.
Common Side Effects
- Drowsiness
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Memory impairment
Risks of Long-Term Misuse
- Cognitive Decline: Long-term use of benzodiazepines has been linked to memory problems and difficulty concentrating.
- Physical Dependence: The body adapts to the drug, and withdrawal symptoms appear when use stops.
- Withdrawal Risks: Symptoms like severe anxiety, insomnia, tremors, and even seizures may occur. This makes quitting “cold turkey” dangerous.
With Ativan vs Xanax, withdrawal can be life-threatening if not medically supervised. Detox should always be done under the care of professionals, often in a treatment center where safety and comfort can be prioritized.
The Role of Ativan and Xanax in Substance Use Disorders
Benzodiazepine misuse is a growing problem in the United States. Many people prescribed Ativan or Xanax start taking more than directed because their anxiety symptoms persist or because they like the calming sensation. Others obtain the drugs illegally to self-medicate or enhance the effects of alcohol or opioids.
Unfortunately, this can quickly spiral into dependence. Both Ativan and Xanax are often found in cases of polysubstance abuse, where individuals combine them with alcohol, opioids, or stimulants. This dramatically increases overdose risk.
In treatment programs, clients frequently report that Ativan vs Xanax misuse started as a way to “take the edge off” daily stress but escalated into something they could not control. Recognizing this progression is crucial in guiding people toward recovery.
Choosing Between Ativan vs Xanax: A Recovery Perspective
Doctors often prescribe Ativan or Xanax based on medical need, but in addiction recovery, the choice looks very different. The goal isn’t about choosing which is “better” for symptom relief—it’s about addressing the risks of misuse and creating sustainable recovery strategies.
Factors Professionals Consider
- History of Substance Use: If a person has struggled with drug or alcohol addiction, prescribing benzodiazepines can be risky.
- Underlying Mental Health Conditions: Anxiety and panic disorders need treatment, but often safer, non-addictive alternatives (like SSRIs, therapy, or holistic methods) are considered first.
- Environment: Access to triggers and social influences can make relapse more likely, especially if benzodiazepines are part of the recovery picture.
In recovery, the focus isn’t just on Ativan vs Xanax, but on exploring healthier coping mechanisms that don’t fuel dependence.
Safer Alternatives to Ativan and Xanax
For people in recovery—or those at risk of developing a substance use disorder—other approaches may be safer and more effective in the long run:
- Non-addictive Medications: SSRIs (like Zoloft or Prozac) or buspirone are often prescribed for anxiety without the same risk of dependence.
- Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) teaches individuals to reframe anxious thoughts and develop healthier coping skills.
- Holistic Approaches: Yoga, meditation, breathwork, and mindfulness can help regulate anxiety without substances.
- Lifestyle Changes: Improving sleep hygiene, exercise, and diet can all reduce anxiety symptoms naturally.
By exploring these alternatives, treatment centers help individuals move away from the risks associated with Ativan vs Xanax.

Detox and Withdrawal: What to Expect
One of the most difficult aspects of recovery from Ativan or Xanax misuse is withdrawal. Because both drugs alter brain chemistry, stopping suddenly can trigger intense and sometimes dangerous symptoms.
Possible Withdrawal Symptoms
- Severe rebound anxiety
- Insomnia
- Sweating and shaking
- Muscle pain
- Seizures (in extreme cases)
Medical detox programs gradually taper the drug under supervision, ensuring safety and reducing discomfort. This is often the first step toward recovery when addressing benzodiazepine addiction.
When discussing Ativan vs Xanax, both require careful, structured detox programs. The difference usually lies in how quickly symptoms emerge and how long they last, since Xanax leaves the body faster than Ativan.
Long-Term Recovery After Benzodiazepine Misuse
Detox is only the beginning. Sustainable recovery from Ativan or Xanax addiction involves ongoing support and treatment.
Elements of Long-Term Recovery
- Inpatient or Outpatient Rehab: Structured programs that provide therapy, group support, and relapse prevention strategies.
- Dual Diagnosis Care: Many people with benzodiazepine addiction also struggle with anxiety, depression, or trauma. Treating both addiction and mental health is key.
- Support Groups: Groups like Narcotics Anonymous or SMART Recovery provide community support and accountability.
- Aftercare Programs: Continued counseling, sober living arrangements, and ongoing check-ins help prevent relapse.
A recovery-focused approach doesn’t just ask, “Which is better—Ativan vs Xanax?” Instead, it reframes the question: “How can we help someone build a life free from the need for either?”
Frequently Asked Questions About Ativan vs Xanax
1. Which works faster—Ativan or Xanax?
Xanax acts faster, but its short half-life makes it more addictive. Ativan lasts longer, which may reduce frequent dosing, but both carry dependence risks.
2. Is it safe to take Ativan and Xanax together?
No. Combining them increases the risk of overdose, respiratory depression, and addiction.
3. Can I stop taking Ativan or Xanax on my own?
Stopping abruptly is dangerous. Always seek medical supervision during detox.
4. Are there safer options for treating anxiety in recovery?
Yes—non-addictive medications, therapy, and holistic practices are often better suited for people in recovery.
Final Thoughts: Ativan vs Xanax in the Recovery Journey
For those in recovery, the debate around Ativan vs Xanax isn’t just about which drug works better—it’s about understanding their risks, how dependence develops, and what alternatives exist. Both Ativan and Xanax can provide short-term relief for anxiety, but they also carry a significant potential for addiction.
Recovery programs emphasize not just detoxing from these substances but also teaching healthier coping mechanisms and building a foundation for long-term sobriety.
If you or a loved one is struggling with benzodiazepine use, know that help is available. With medical support, therapy, and community, recovery is possible—and life beyond Ativan or Xanax can be healthier, calmer, and more fulfilling. For more helpful information, contact us at Knoxville Recovery Center or call us directly for immediate assistance.